Skip or ignore execution of tests in TestNG at run time. In this section Let’s Understand, How to Skip Testcase in TestNG and What are the Different ways to Skip Testcases in TestNg Before Skipping test Follow How to install the TestNG Plugin in Eclipse IDE.
TestNG Provides the Functionality to Skip or Ignore Testcases, Generally, the Tester Skips the test cases based on their Requirement or to Follow Different TestFlow to Check the Application.
There are Two Ways to Skip Testcase in TestNG
1. Skipping Testcases Using @Test(enabled=false)
2. Skipping Testcases Using throw new SkipException("This Testcase is Skipped Deliberately");
Skip Test in TestNG Using @Test(enabled=false)
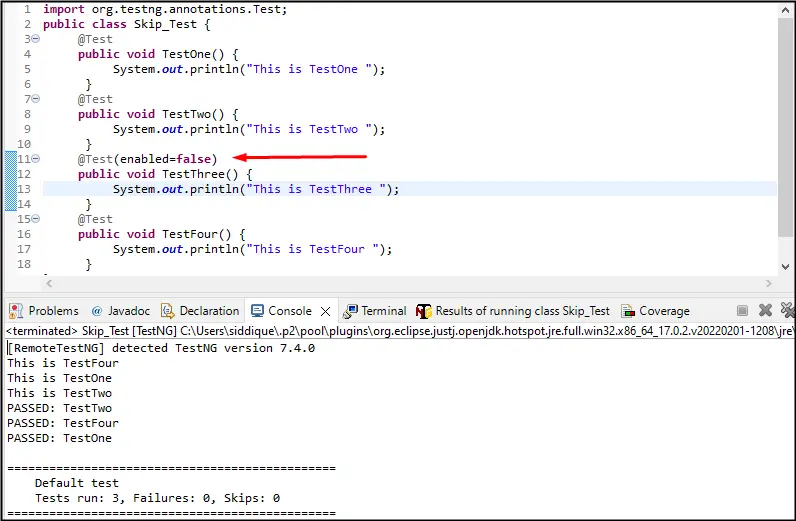
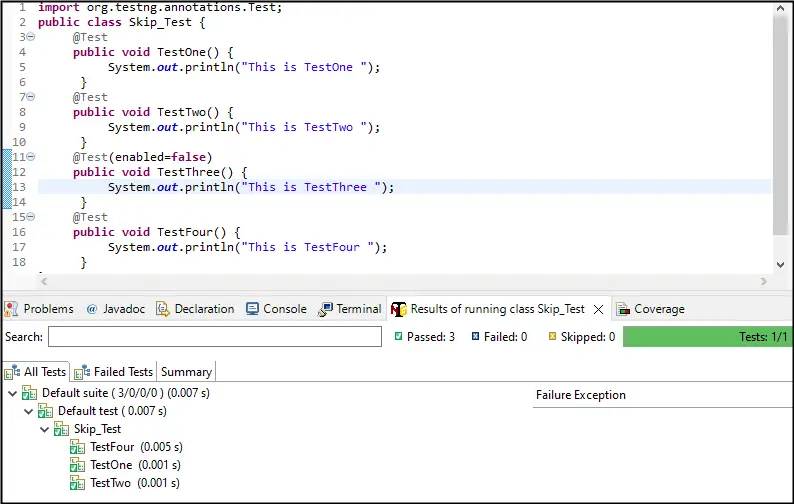
Create Class Name Skip_Testand create four Testcases Named as Testone(),TestTwo(),TestThree()and TestFour() and added prints statements to each Testcase to display the execution Flow and Skip TestThree()Testcase Using @Test(enabled=false)
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Skip_Test {
@Test
public void TestOne() {
System.out.println("This is TestOne ");
}
@Test
public void TestTwo() {
System.out.println("This is TestTwo ");
}
@Test(enabled=false)//This Testcase Would Be Skipped and ignored duing execution
public void TestThree() {
System.out.println("This is TestThree ");
}
@Test
public void TestFour() {
System.out.println("This is TestFour ");
}
}
Code Explanation
@Test(enabled=false)//This Testcase Would Be Skipped and ignored during execution
public void TestThree() { System.out.println("This is TestThree ");
Using the @Test(enabled=false) the test case Would be Ignored and Skipped during the Execution by the compiler
Output
Skip Test in TestNG Using SkipException
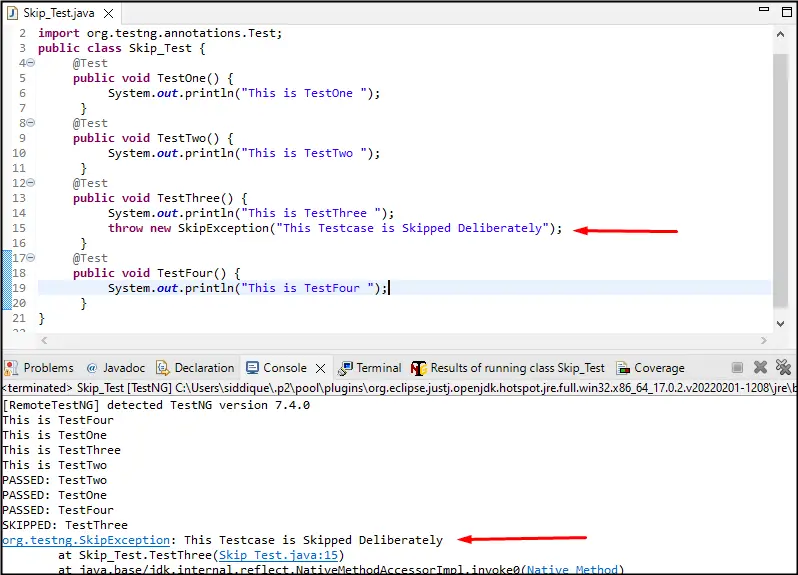
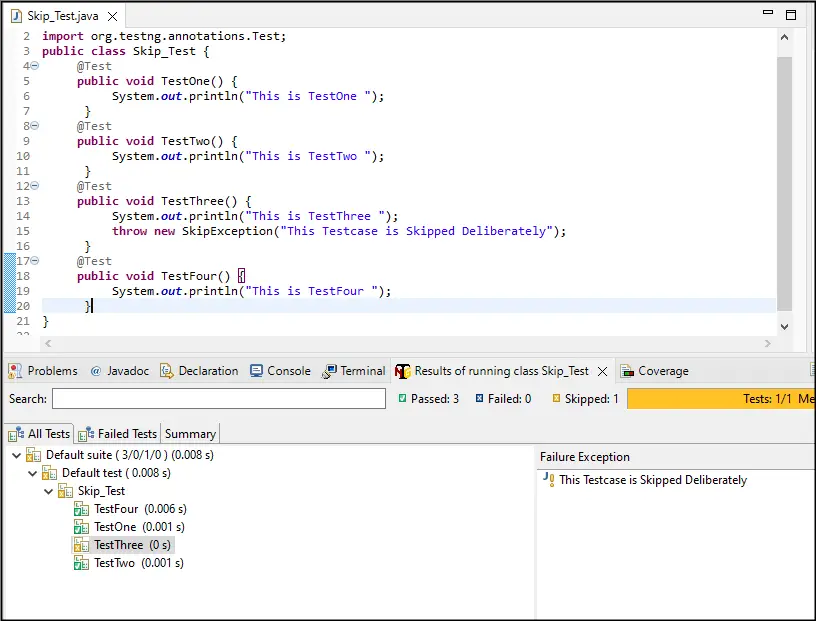
Create Class Name Skip_Testand create four Testcases Named as Testone(),TestTwo(),TestThree()and TestFour() and added prints statements to each Testcase to display the execution Flow and Skip TestThree()Testcase Using throw new SkipException();
Code
import org.testng.SkipException;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Skip_Test {
@Test
public void TestOne() {
System.out.println("This is TestOne ");
}
@Test
public void TestTwo() {
System.out.println("This is TestTwo ");
}
@Test
public void TestThree() {
System.out.println("This is TestThree ");
throw new SkipException("This Testcase is Skipped Deliberately");//this Testcase Would Be Skipped as an Exception During Execution
}
@Test
public void TestFour() {
System.out.println("This is TestFour ");
}
}
Code Explanation
throw new SkipException("This Testcase is Skipped Deliberately");
Using the throw new SkipException();
The Testcase Can be skipped and an Exception would be Throw During Execution Also we can Set an Error string into it.
Output
We Have Successfully Skipped Testcase in TestNG.
