A TEST SUITE is a collection of test cases. In automated testing, it can mean a collection of test scripts. In a test suite, the test cases/scripts are organized in a logical order. For example, the test case for registration will precede the test case for login.
A Test case can be added to multiple test suites and test plans. After creating a test plan, test suites are created which in turn can have any number of tests.
Test suites are created based on the cycle or based on the scope. It can contain any type of tests, viz – functional or Non-Functional.
ISTQB Definition
Test suite: A set of test scripts or test procedures to be executed in a specific test run.
When you have hundreds/thousands of test cases, a test suite allows you to categorize them in a way that matches your planning or analysis needs.
For example, you could have a test suite for each of the core features of the software or you could have a separate test suite for a particular type of testing (for example, smoke test suite or security test suite).
An example of a test suite for purchasing a product could comprise of the following test cases:
Test Case 1: Login
Test Case 2: Add Products
Test Case 3: Checkout
Test Case 4: Logout
Occasionally, test suites are used to group similar test cases together. A system might have a smoke test suite that consists only of smoke tests or a test suite for some specific functionality in the system. It may also contain all tests and signify if a test should be used as a smoke test or for some specific functionality.
In software engineering, it (more formally known as a validation suite) is a collection of test cases that are intended to be used as input to a software program to show that it has some specified set of behaviors (i.e., the behaviors listed in its specification).
It often also contains detailed instructions or goals for each collection of test cases and information on the system configuration to be used during testing. A group of test cases may also contain prerequisite states or steps, and descriptions of the following tests.
Collections of test cases are sometimes incorrectly termed a test plan. They may also be called a test script, or even a test scenario.
Test Suite Diagram
A test plan is sub-categorized into test suites and these test suites may further be subdivided into the number of test cases. This overall study of test suites and test cases provides a better test plan.
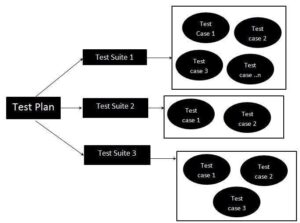
Features of Test Suite
Test suites offer various advantages to the team of testers as well as the organization they are working for. Therefore, to offer you a better insight into its qualities mentioned below are some of its important features:
- Test suites are created after the test plan.
- It includes a number of tests and test cases.
- Describes the goals and objectives of test cases.
- It has test parameters, such as application, environment, version, etc.
- One can create test suites on the basis of the test cycle as well as the test scope.
- It consists of various types of tests, such as functional or non-functional.
- Test suite helps increase the productivity of testing by providing a means to rapidly test and review the
- software under test (SUT).
- It can be used for various automated tools like jUnit, Selenium, etc.
Test Suite Template
Since the importance of the test suite is immense in Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), it is vital for software testers to follow a standardized template to create a test suite and define the various aspects covered by it.
These templates can either be predefined or can be created by the team as per the requirements of their project. Hence, to help you with the process, here is a sample of the test suite template.
- Test Suite Summary: As suggested by the title, this section of the template consists of a detailed summary of the test suite. It might also include categories of test suites, to further improve the comprehensiveness of the test suite.
- Test Suite Design: Again, this section offers details about the design of the test suite, along with various suggestions to enhance the quality and coverage of the testing.
- Formal Review: Once the test suite summary and design are defined, the team performs a formal review, which helps organizations in making their business processes conform to standards and regulations of the industry.
- Pre-condition & Post-condition: These define and check the various requirements that are needed to be fulfilled before and after executing the test suite.
- Expected Results: Here, the team defines the conditions that are required to be fulfilled for a test suite to be considered successful. These expected results are then compared with the actual result to further validate the success of a test suite.
- Risk Assessment/Analysis: The team finally identifies and analyzes the various risks associated with the test suite, which can impact the process of testing and hinder the team to get expected outcomes.
- Test Cases: This section of the template consists of test cases and their associated test environment, which are then executed by the team to validate various aspects of the software under test (SUT).
- Documents & Reports Includes all the documents and reports that are either associated or attached with test suites, such as screenshots, reports, execution recorder, and other important material.
Test Suite Example
We create a test scenario as:
- The user must be logged
- Move to the “upload photos” page
- Click the “upload” button
- Select photos
- Upload them
Now, this scenario should be divided into detailed test cases, for example:
- Check the logged user possibility to go to the “upload photos” page
- Check the not logged user possibility to go to the “upload photos” page
- Check whether the user can click the “upload” button
- Is it opens a form to select a photo and the possibility to close it
- What happens if you do not select photos, choose another file format (for example video), choose photos of the maximum size, and so on
- Check the possibility to upload photos
- Check if the photo is saved
- Possibility to reload or delete photos
- What happens with photos in the case of the disappearance of the Internet or the device is switched off
- Are all buttons displayed correctly at another location or on different operating systems (if any difference)
And so on. The number of test cases depends on the experience and imagination of the tester.
Therefore, the process of writing test cases starts from forming a test scenario or user story, and then it can be divided to check different occasions.
Difference Between Test Plan, Test Suite, Test Case, and Test Scenarios
|
Test Plan |
Test Suite | Test Case |
Test Scenarios |
| 1. Test plan is a document that defines the scope, objective, and strategy of testing. | 1. Prepared after test plan, test suite consists of a collection of test cases. | 1. Test case is an important document that consists of various crucial details about testing. | 1. Test scenarios or test condition is any functionality of the software that can be tested. |
| 2. It is of three types, level specific, type specific, master test plan. | 2. It is of two types, abstract and executable test suites. | 2. These are of two types, formal test cases and informal test case. | 2. It is performed from the perspective of the end users. |
| 3. It follows a standardized template, which offers details about the testing process. | 3. Test suites define the objective and goal of test cases that are intended to test the software product. | 3. It defines a set of conditions that help verify the compliance of the software with specified functionality. | 3. It defines the various operations that are performed by the team on the software product. |
| 4. It is derived from Product Description, Software Requirement Specifications (SRS), or Use Case Document. | 4. Separate test suites offer great advantages to team and it created testing to be hassle free, flexible, agile. | 4. These are derived from the test scenarios and are designed on the basis of Software Requirement Specification (SRS). | 4. They are derived from the use cases and they ensure complete test coverage. |