As of now, we have seen everything about the Servlet its classes, interfaces, cookies, session, Database connectivity, etc. In this article, we will make a Registration application using the Servlet and MySQL database.
Registration Example using Servlet
We will be using an MYSQL database, so first create a database registration_form and then create a table user_register in the database.
create database registration_form
use registration_form
create table user_register(Id int Auto_Increment,primary key(id),Name varchar(20) NOT NULL,
-> Email varchar(30) NOT NULL,userName varchar(30) NOT NULL,password varchar(20) NOT NULL, Unique key(userName));
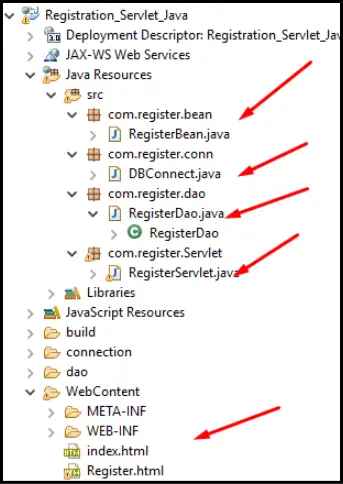
I have created a folder structure as shown below to follow the basic coding practice in the Eclipse IDE.
Now, We will create index.html and Register.html for the View.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1"> <title>Servlet</title> </head> <body> <h1 align="center"><a href="Register.html">Register</a></h1> </body> </html>
Register.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<style>
body {
background-image:
url('https://image.shutterstock.com/image-photo/lime-retro-pastel-paper-background-260nw-598436903.jpg');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="RegisterServlet" method="post">
<h1 align="center" style="margin-top: 5%">Registration Form</h1>
<table align="center" style="margin-top: 10%">
<tr>
<td>Name</td>
<td><input type="text" name="name"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Email Id</td>
<td><input type="email" name="email"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>UserName</td>
<td><input type="text" name="uname"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password</td>
<td><input type="password" name="pass"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Confirm Password</td>
<td><input type="password" name="cpass"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Submit" id="button-1" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Now we will create a Database connection class for initializing the database
DBConnect.java
package com.register.conn;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBConnect {
public static Connection getConn() {
Connection con = null;
String loadDriver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String dbURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Registration_form";
String dbUSERNAME = "root";
String dbPASSWORD = "root";
try {
Class.forName(loadDriver);
con = DriverManager.getConnection(dbURL, dbUSERNAME, dbPASSWORD);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
}
Now, we will create a Bean class. As we know JavaBeans are classes that encapsulate many objects into the single bean(Single object).
RegisterBean.java
package com.register.bean;
public class RegisterBean {
String Name;
String EMail;
String userName;
String pasword;
public RegisterBean(String name, String eMail, String userName, String pasword) {
super();
Name = name;
EMail = eMail;
this.userName = userName;
this.pasword = pasword;
}
public RegisterBean() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
public String getEMail() {
return EMail;
}
public void setEMail(String eMail) {
EMail = eMail;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPasword() {
return pasword;
}
public void setPasword(String pasword) {
this.pasword = pasword;
}
}
Now we will create a Dao class (Data Access Object). It involves the business logic for database operation like insert, update, delete (basically the CRUD operation of the database).
RegisterDao.java
package com.register.dao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import com.register.bean.RegisterBean;
import com.register.conn.DBConnect;
public class RegisterDao {
public String Regiterindb(RegisterBean bean) {
Connection con = DBConnect.getConn();
String sql = "insert into user_register(Id,Name,Email,userName,password) values (NULL,?,?,?,?) ";
int i = 0;
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = con.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, bean.getName());
preparedStatement.setString(2, bean.getEMail());
preparedStatement.setString(3, bean.getUserName());
preparedStatement.setString(4, bean.getPasword());
i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (i != 0) {
return "User is registered";
} else {
return "Error!!!!";
}
}
}
Then, we will create a Servlet class
RegisterServlet.java
package com.register.Servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.register.bean.RegisterBean;
import com.register.dao.RegisterDao;
public class RegisterServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public RegisterServlet() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("inside post");
response.setContentType("text/html");
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String email = request.getParameter("email");
String username = request.getParameter("uname");
String password = request.getParameter("pass");
RegisterBean bean = new RegisterBean(name, email, username, password);
RegisterDao dao = new RegisterDao();
String result = dao.Regiterindb(bean);
if (result.equals("User is registered")) {
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("index.html");
dispatcher.include(request, response);
} else {
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher("Register.html");
dispatcher.include(request, response);
}
}
}
create web.xml for the mapping of the URL.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>Register Servlet Demo</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>RegisterServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.register.Servlet.RegisterServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>RegisterServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/RegisterServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
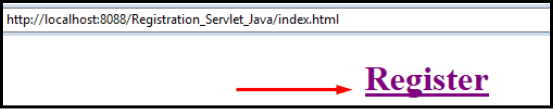
When we will run this application from the index.html page we will get the following output:
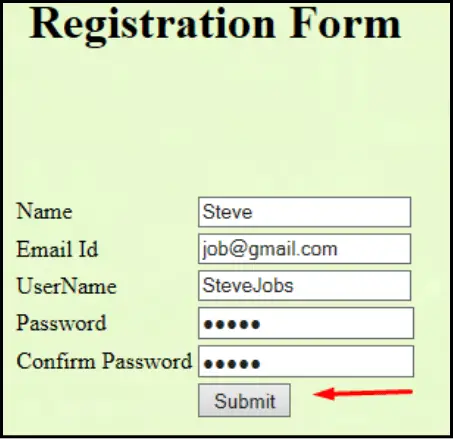
Now Click on Submit and check whether the data is inserted into the database. To check, let’s see in the database.
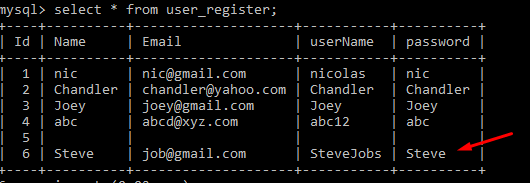
Thus we can create a Registration in Servlet by using the above steps.
Login Example in Servlet
We will be using the same database as we used for the Registration i.e user_register and we will fetch the username and password from it for Login Example.
I have created a folder structure as shown below to follow the basic coding practice in the Eclipse IDE.
Now, We will create Login.html and Welcome.html for the View.
Login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<style>
body {
background-image:
url('https://image.shutterstock.com/image-photo/lime-retro-pastel-paper-background-260nw-598436903.jpg');
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form action="LoginServlet" method="post">
<h1 align="center" style="margin-top: 5%">Login Form</h1>
<table align="center" style="margin-top: 10%">
<tr>
<td>UserName</td>
<td><input type="text" name="uname"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password</td>
<td><input type="password" name="pass"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Confirm Password</td>
<td><input type="password" name="cpass"></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Submit" id="button-1" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Welcome.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="ISO-8859-1"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h1>Login Successfully!!!!</h1> </body> </html>
Now we will create a Database connection class for initializing the database
DBConnect.java
package com.login.DBconn;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBConnect {
public static Connection getConn() {
Connection con = null;
String loadDriver = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
String dbURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Registration_form";
String dbUSERNAME = "root";
String dbPASSWORD = "root";
try {
Class.forName(loadDriver);
con = DriverManager.getConnection(dbURL, dbUSERNAME, dbPASSWORD);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
}
Now, we will create a Bean class. As we know JavaBeans are classes that encapsulate many objects into a single bean(Single object).
LoginBean.java
package com.login.bean;
public class LoginBean {
private String userName;
private String password;
public LoginBean(String userName, String password) {
super();
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
}
public LoginBean() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
Now we will create a Dao class (Data Access Object). It involves the business logic for database operation like insert, update, delete (basically the CRUD operation of the database).
LoginDao.java
package com.login.LoginDao;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import com.login.DBconn.DBConnect;
import com.login.bean.LoginBean;
public class LoginDao {
public boolean vaildate(LoginBean bean)
{
boolean result = false;
Connection connection=DBConnect.getConn();
String sql="select * from user_register where userName=? and password=?";
try {
PreparedStatement ps=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, bean.getUserName());
ps.setString(2, bean.getPassword());
ResultSet rs=ps.executeQuery();
result=rs.next();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
Then, we will create a Servlet class
LoginServlet.java
package com.login.Servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.login.LoginDao.LoginDao;
import com.login.bean.LoginBean;
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet()
*/
public LoginServlet() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
response.setContentType("text/html");
String uname=request.getParameter("uname");
String pass=request.getParameter("pass");
LoginBean bean=new LoginBean();
LoginDao dao=new LoginDao();
bean.setUserName(uname);
bean.setPassword(pass);
if(dao.vaildate(bean))
{
response.sendRedirect("Welcome.html");
}
else
{
response.sendRedirect("Login.html");
}
}
}
create web.xml for the mapping of the URL.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>Login_Form_usingServlet</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.login.Servlet.LoginServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>LoginServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/LoginServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
When we will run this application from the Login.html page we will get the following output:
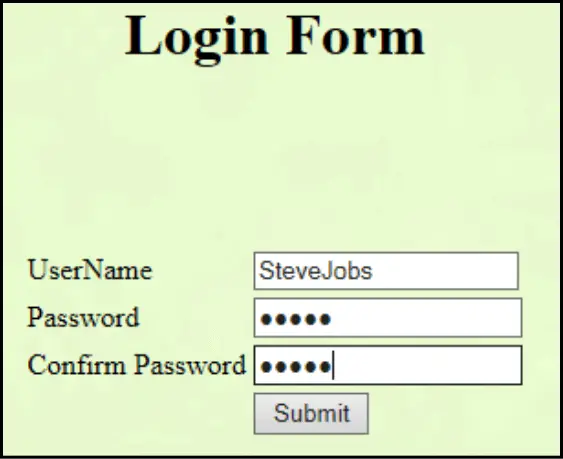
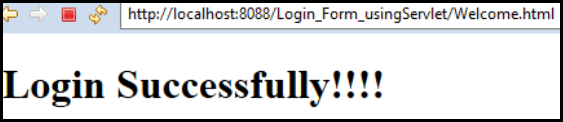
Thus we have created a Login Form using Servlet by using the above steps.